Visit us in San Francisco
Academic standards. Pioneering research. Personalized care. Start your journey at the UCSF Center for Reproductive Health, located in Northern California's San Francisco Bay Area.
We are currently booking new patient appointments. Please fill out our form to get started.
The menstrual cycle is a rhythmic sequence of events reflecting communication between the brain, ovary and uterus.
This is called the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian (HPO) axis. Hormones produced in the hypothalamus and pituitary gland (brain) and follicles (ovary) coordinate the cycle events.
Understanding the menstrual cycle unlocks a better understanding of why your doctor gives you certain medications to promote fertility. Disorders of the menstrual cycle can also contribute to infertility.
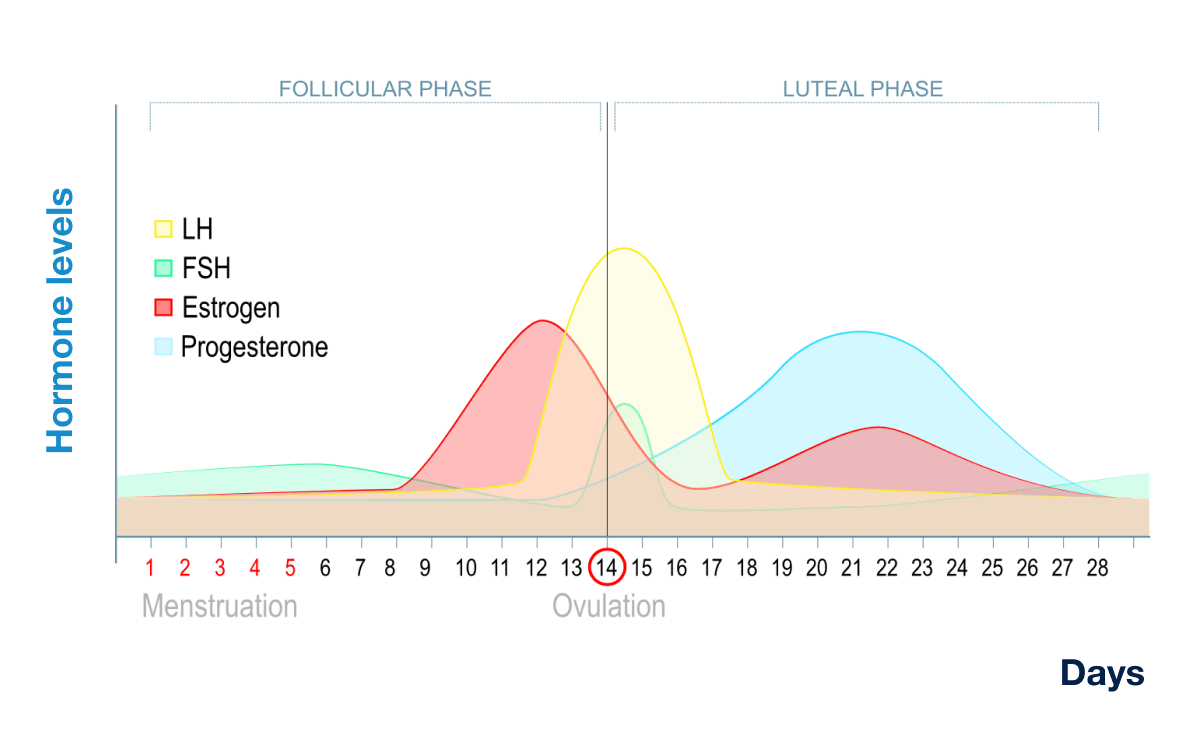
On average, a menstrual cycle is 28 days long, but can range from 25-35 days. The cycle length is measured from the first day of bleeding in one cycle (CD1, cycle day 1) to the first day of bleeding in a subsequent cycle. There are two main phases of the menstrual cycle, the follicular phase and the luteal phase. Ovulation occurs approximately 14 days before the onset of the next menstrual period. For example, in a 28 day cycle, ovulation typically occurs around day 14; in a 26 day cycle it occurs around day 12, and in a 30 day cycle it occurs around day 16. Ovulation demarcates the transition from the follicular phase to the luteal phase.
The follicular phase begins with the first day of bleeding (CD1). It is called the follicular phase because this is when the ovarian follicles, fluid filled structures containing one egg each, grow. Follicular growth is driven by the appropriately named follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) which is produced by the pituitary gland.
In a typical menstrual cycle, communication between the brain and ovary leads to the development of a single “dominant follicle”, which will ultimately release its egg at ovulation. As the dominant follicle grows under the influence of FSH, it starts to produce increasing levels of estrogen.
Estrogen has two basic functions in the menstrual cycle. One is to develop the uterine lining, which increases in thickness during the follicular phase. The second is to trigger the surge of another hormone, luteinizing hormone (LH), which is released from the pituitary gland when estrogen levels are at their highest, prior to ovulation. This LH “surge” leads to ovulation of the egg (oocyte) from the dominant follicle. LH is also the hormone that is picked up by home ovulation predictor kits.
The most fertile period is from the three days leading up to ovulation through the day of ovulation. This is the also called the “fertile window.”
After ovulation, the luteal phase begins. It is called the luteal phase because the ruptured follicle that released the egg turns into a new endocrine organ called the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum produces the hormone progesterone. Progesterone causes the uterine lining to mature and become supportive for implantation of an embryo, and is also necessary to sustain an early pregnancy once implantation has occurred.
If pregnancy occurs, the uterine lining is maintained and progesterone levels stay elevated as the embryo develops.
If pregnancy does not occur, there is a drop in progesterone levels, which results in shedding of the endometrial lining and transitioning into the next menstrual cycle.
Academic standards. Pioneering research. Personalized care. Start your journey at the UCSF Center for Reproductive Health, located in Northern California's San Francisco Bay Area.
Academic standards. Pioneering research. Personalized care. Start your journey at the UCSF Center for Reproductive Health, located in Northern California's San Francisco Bay Area.






